- Menu
- Search For Product Models
Search For Product Models
- cn
1. Introduction
A Stainless Steel Fusion Bond Heat Exchanger is a compact plate heat exchanger in which stainless steel plates are permanently joined using a fusion bonding (diffusion bonding) process.
Unlike traditional brazed or gasketed plate heat exchangers, this technology does not use copper brazing materials or elastomer seals, resulting in an all-stainless-steel construction.
Fusion bonded heat exchangers are specifically designed for applications that demand high cleanliness, corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and long-term operational reliability.
2. Fusion Bonding Technology
Fusion bonding is a solid-state joining process characterized by:
Stacking precision-formed stainless steel plates
Applying high temperature and pressure
Creating a metallurgical bond at the molecular level
No melting of base material
No filler metals or brazing alloys
The result is a monolithic stainless steel heat exchanger, where the plates are permanently bonded without introducing dissimilar materials into the structure.
This eliminates risks associated with galvanic corrosion, filler material degradation, and material incompatibility.
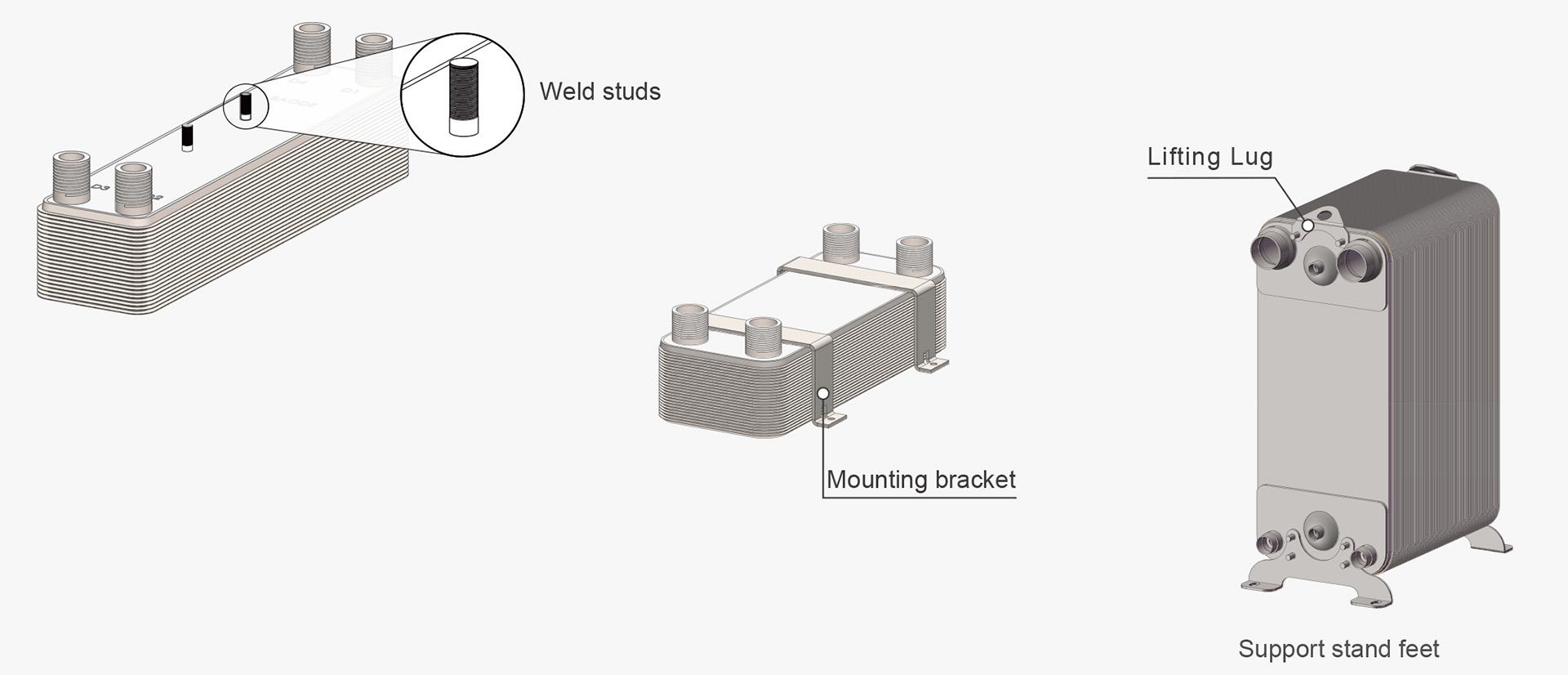
3. Construction Features
Key construction characteristics include:
100% stainless steel plates and bonding zones
Chevron or herringbone plate patterns for enhanced turbulence
Compact, gasket-free design
Uniform bonding across plate contact areas
High resistance to pressure and thermal fatigue
Because bonding occurs over large surface areas, fusion bonded heat exchangers exhibit excellent mechanical integrity and long service life.
4. Performance Advantages
High Corrosion Resistance
No copper or nickel exposure to process fluids
Suitable for aggressive or sensitive media
Compatible with deionized water, ammonia, CO₂, and other demanding fluids
Clean and Hygienic Design
No brazing materials that could leach into the fluid
Suitable for clean systems and high-purity applications
Smooth internal surfaces help reduce fouling
High Mechanical Strength
Excellent resistance to pressure fluctuations
Withstands frequent thermal cycling
Stable performance under dynamic operating conditions
Compact and Efficient
High heat transfer efficiency due to optimized plate geometry
Smaller footprint compared to shell-and-tube designs
Reduced installation space requirements
5. Comparison with Other Heat Exchanger Types
Feature Fusion Bond Brazed Plate Gasketed Plate
Sealing method Solid-state metal bond Copper brazing Elastomer gaskets
Dissimilar metals None Yes Possible
Maintenance Maintenance-free Maintenance-free Periodic gasket replacement
Temperature resistance High High Limited by gasket material
Chemical compatibility Excellent Limited by brazing alloy Limited by gasket material
6. Typical Applications
Stainless steel fusion bond heat exchangers are widely used in:
Refrigeration and heat pump systems
Industrial process heating and cooling
District heating and cooling networks
Clean water and ultrapure water systems
Chemical and pharmaceutical processes
Applications where copper or elastomers are not acceptable
7. Operational Reliability
The absence of gaskets and brazing materials provides several operational advantages:
Minimal risk of internal leakage
Stable long-term performance
Reduced sensitivity to pressure shocks
Lower total cost of ownership over the product lifecycle
Fusion bonded heat exchangers are particularly well suited for continuous operation and critical system applications.
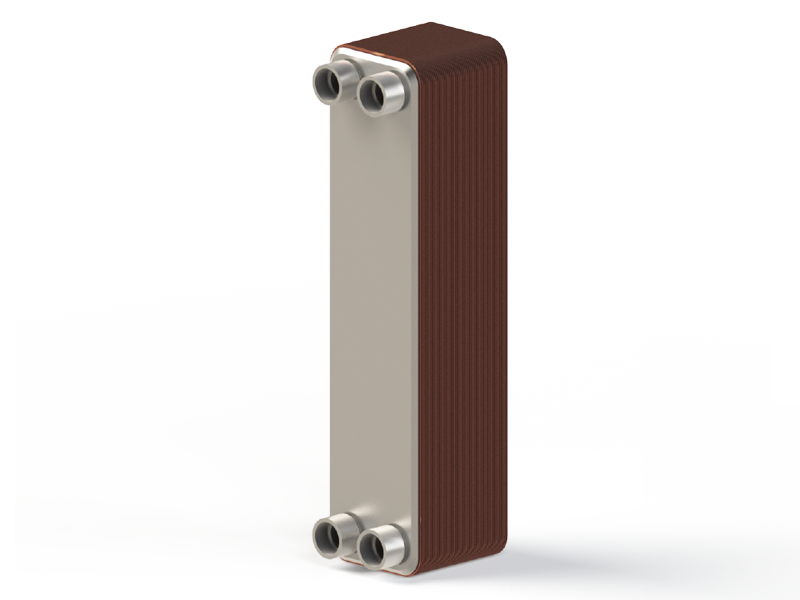 *Performance Comparison at a Glance
*Performance Comparison at a Glance
Copper Brazed BPHE
• Max Temp: Up to 200°C
• Corrosion Resistance: Moderate
• Chemical Compatibility: Limited
• Thermal Efficiency: High
• Hygiene: Moderate
• Ion Contamination: Possible
• Brazing Integrity: May degrade
• Cost: Lower initial cost
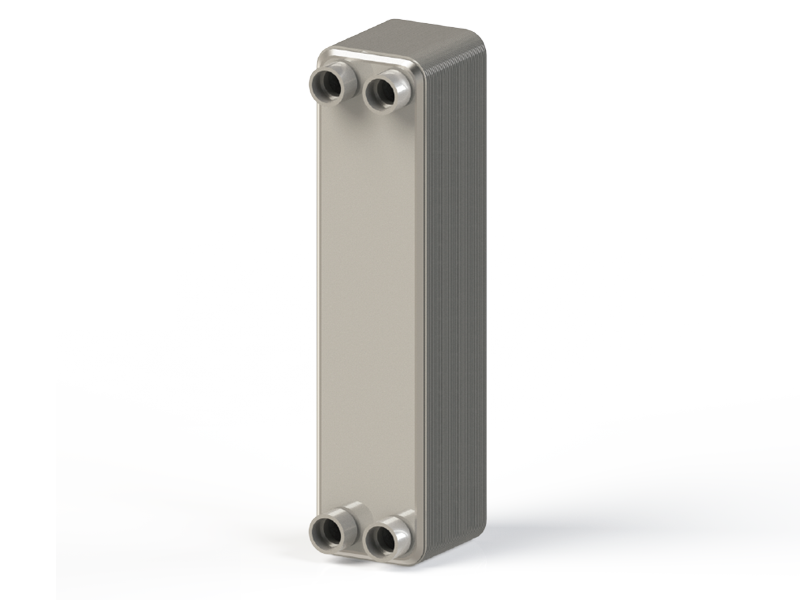

Stainless Brazed BPHE
• Max Temp: Up to 400°C
• Corrosion Resistance: Excellent
• Chemical Compatibility: Broad
• Thermal Efficiency: Slightly lower
• Hygiene: High
• Ion Contamination: None
• Brazing Integrity: Excellent
• Cost: Higher upfront
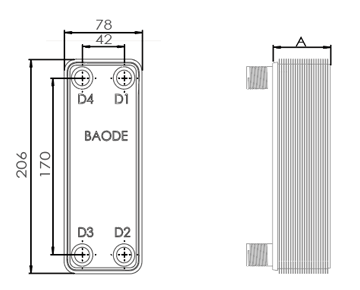 Dimensions in mm
Dimensions in mm

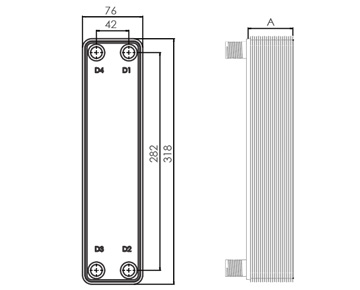 Dimensions in mm
Dimensions in mm


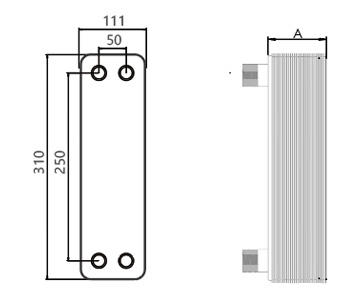 Dimensions in mm
Dimensions in mm


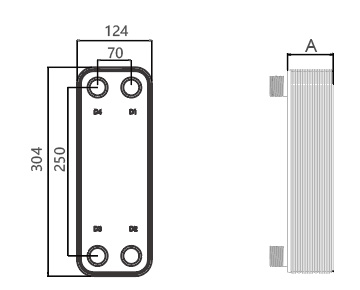 Dimensions in mm
Dimensions in mm


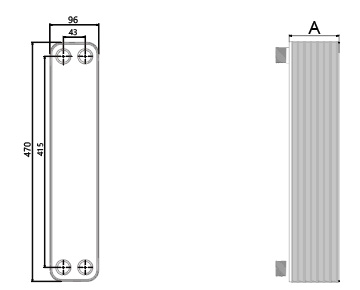 Dimensions in mm
Dimensions in mm


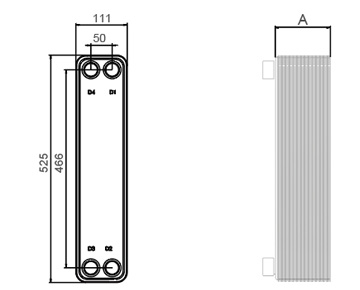 Dimensions in mm
Dimensions in mm


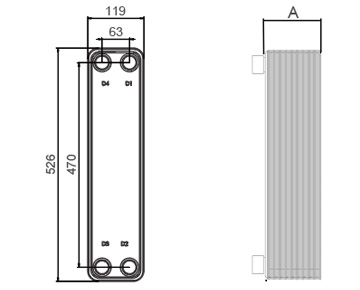 Dimensions in mm
Dimensions in mm


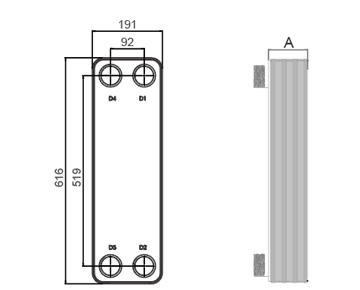 Dimensions in mm
Dimensions in mm


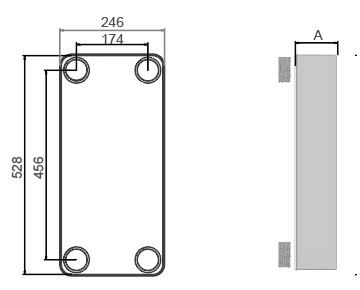 Dimensions in mm
Dimensions in mm


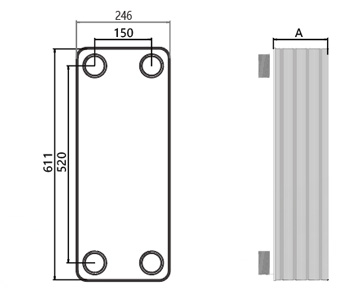 Dimensions in mm
Dimensions in mm


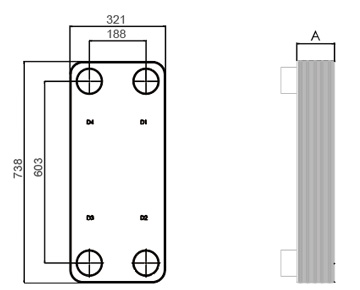 Dimensions in mm
Dimensions in mm